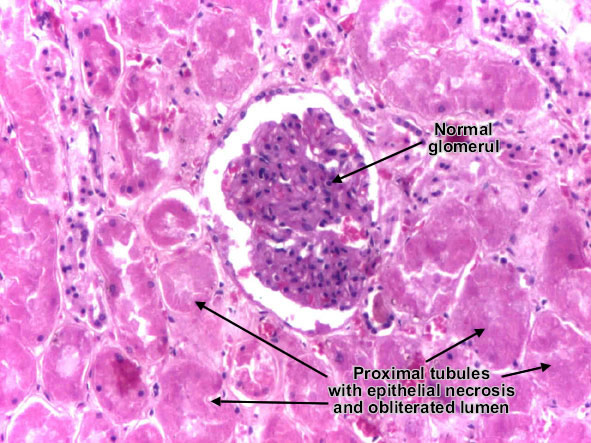
Toxic tubular necrosis
Acute tubular necrosis is a pathological entity characterized by destruction of tubular epithelial cells, followed by acute renal failure (oliguria, proteinuria, blood retention of urea and creatinine).
Depending on etiology, there are two types of acute tubular necrosis :
- toxic acute tubular necrosis, after ingestion or inhalation of toxic substance ethylene glycol, mercury, lead, carbon tetrachloride, methyl alcohol, nephrotoxic drugs
- ischemic acute tubular necrosis - in shock
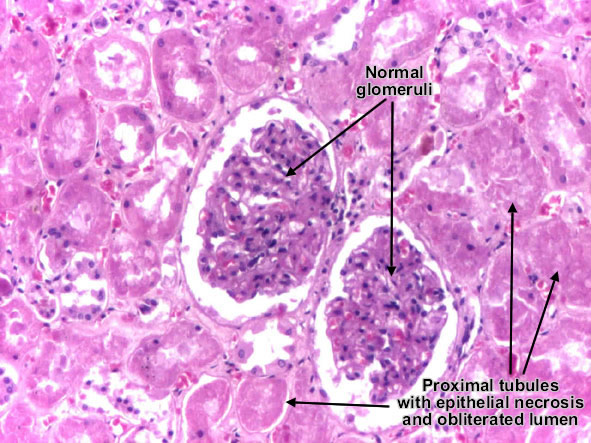
Toxic acute tubular necrosis is characterized by proximal tubular epithelium necrosis (no nuclei, intense eosinophilic homogenous cytoplasm, but preserved shape) due to interference of ingested toxic agents (poisons, organic solvents, drugs, heavy metals) with epithelial cell metabolism. Necrotic cells fall into the tubule lumen, obliterating it, and determining acute renal failure (oligo-anuria). Basement membrane is intact, so the tubular epithelium regeneration is possible, if the patient survives. The interstitium and glomeruli are not affected. (H&E, ob. x20)